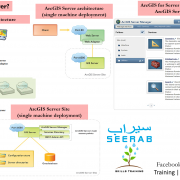
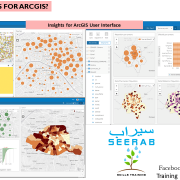
Most Famous & Used GIS File Format
The ESRI Shapefile (known here as the #ESRI #Shapefile format), stores nontopological geometry and attribute information for the spatial features in a data set.
The Shapefile format is open and popular for data transfer. An initial state format during map and shape digitization output, employed as a middle state format by many programs and publishers, and used for data transfer between GIS applications. Shapefiles can be created by exporting any data source to a shapefile, digitizing shapes directly, using programming software, or writing directly to the shapefile specifications by creating a program.
A shapefile consists minimally of a main file, an index file, and a dBASE table. The shapefile format can support point, line, and area features. Area features are represented as closed loop, double-digitized polygons. Instances of the Shapefile format have often been used as a data exchange format from ESRI formats to non-ESRI applications.
Must have component: Main file (.shp) and index file (.shx). Shape_DBF, dBASE Table for ESRI Shapefile (DBF).
May have component: Optional component files include files with the following extensions: .sbn; .sbx; .atx; .fbn; .fbx; .ain; .aih; .ixs; .mxs; prj; xml; cpg
The cluster of files is typically stored in the same file directory or project workspace, with all component files having the same filename (prefix) and identified by individual file extension (suffixes).
Want to build a career learn everyday one new thing … be partner with Seerab so we can help you building it :)